Is data science for you? And if it is, how can you use it to grow your business? 
There’s a lot of talk about how the world is changing and conducting business with it, how we live in an unprecedented time where nothing is the same as before. The main ‘culprit’ is technological advancement and, consequently, the amount of data circulating the world and waiting to be used somehow.
But, is this change so profound that it shook up the foundations of doing business? When you get to the bottom of it, everything really stayed the same. Like Paul Simon wrote, “It isn’t strange after changes upon changes we are more or less the same.” Does it apply here, too?
We do not deny the influence data has on the business world. However, the success of the business still boils down to two questions you need to answer:
To who or who are your customers? It’s still a starting position for any business. Your product could be perfect (or you could think so!), but it doesn’t mean a thing if nobody’s buying it. And the point of business is sales. Therefore, you need to find people who want your product at the price that works for you and them.
What you sell or, in other words, your product. This is another foundation of your business. What you want to sell starts with an idea. But before the product reaches its market, complex work is required, including the product’s development, design, quality check, packaging, pricing, marketing strategy, etc.
These two forces in business are alternating, with your customers influencing your product and vice versa.
Then comes the third part, where the influence of data is seen to a full effect. It’s the way how you do something. You could be doing it the old-fashioned way: tapping into the so-called business instinct, where you don’t need any data, and everything goes well until it goes terribly wrong.
Or you could do it the ‘modern way’, which means using data science to help you make business decisions. The key word here is ‘help’. Data science does precisely that. It’s only a tool that can help you make more good business decisions and keep the bad ones to a minimum. Data science doesn’t replace human reason, it doesn’t make decisions instead of you, and it for sure isn’t perfect. But it can help you make an informed decision, leaving your business instinct to act in situations where data isn’t of any help.
How do you build data science into these business foundations to grow your business? We’re going to look at some examples.
Without knowing your customers, you don’t know what they want and need. Knowing that is essential to know what products to offer. Without that, there are no sales, let alone business growth.
According to a report by Qualtrics, five technologies will impact the market-research industry:
Depending on the type of analytics you’re dealing with, these technologies are used to a different extent.
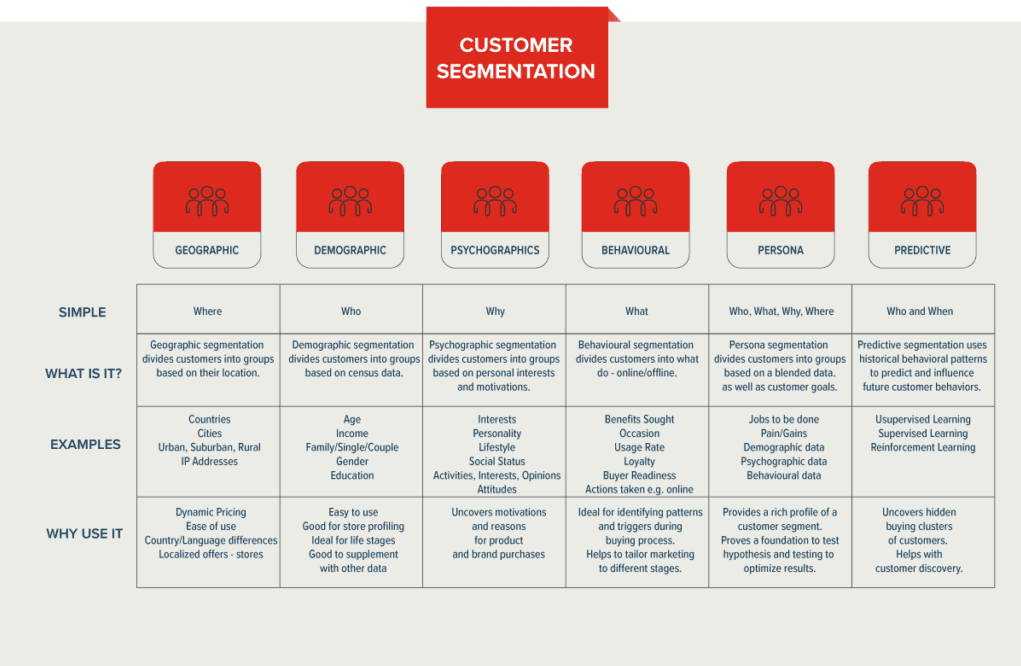
Source: https://www.garyfox.co/customer-segmentation/
Technology allows you to segment your customers in a way not possible until very recently. To do that, you need to collect a vast amount of data.
It can start with simple geographic segmentation, where you collect data such as customers’ countries, cities, and IP addresses.
You can then include demographic data, such as the customers’ age, income, marital status, gender, education, and ethnicity.
Of course, the customer’s willingness to buy your product doesn’t depend just on their location or age. You can go further and collect data about their personality, lifestyle, interests, and opinions.
This is already a considerable amount of data where advanced data analysis and automated statistical analysis can help you deal with data. Data science can make such segmentations much quicker, more precise, and more detailed than you could do by manually segmenting data.
Natural language processing and text analysis can also help you here. The increasing amount of data gets collected in the form of audio files or text written on social media (and the internet in general) in the form of posts, comments, reviews, text messages, etc. Imagine manually going through hundreds, maybe even thousands, of comments by each and every customer. This wouldn’t work!
Data science allows even more sophisticated segmentation based on this data. You can segment your customers according to their behavior, which makes it possible to create customer personas based on the blended data. From there comes the possibility of analyzing what the customers did or said and predicting and influencing their behavior. This is the level where you know your customers better than they know themselves.
Once you know your (potential) customers to the bone, you can target them with greater confidence. This means offering them the right product at the right time and at the right price. Based on your data, you know that you won’t be, for example, offering thrillers to someone who enjoys reading philosophy books. But if you have an excellent new translation of Immanuel Kant’s ‘Critique of Practical Reason’, you might have the right thing for them.
What is their social status? Their income? Maybe they want to buy the book but can’t afford it currently? How about a special deal for the first buyers?
This is all an extension of the customer segmentation. It doesn’t only help to offer your current products to the right market but also can go in another direction—namely, decisions on developing new products that would tap into another market segment.
Keeping your customers is equally important as getting new customers. You’re doing something wrong if you’re acquiring new customers while at the same time losing your current customers at a much quicker rate. There’s no growth there! And it makes new customers reluctant to buy your product or use your services if they know you’re bad at keeping them.
The customers want to see a personal approach that makes them feel understood. And you have the opportunity to understand them by using the extensive data you have on them.
And you want to award their loyalty. Give them something extra. Otherwise, they’ll go to the competitor.
You’d like to know about their satisfaction with the product or service. What they want to be improved regarding the product design, its features, quality, and price. And who doesn’t enjoy some special deals and benefits from time to time?
Again, data here plays a significant role. You can use it to calculate metrics that will explicitly tell you where you stand regarding customer loyalty.
For example, the Net Promoter Score indicates how customers feel about your brand and if they’re willing to recommend it to their family and friends.
Another way to measure loyalty could be repeat purchases. The company internally defines what a repeated purchase is in terms of the number of purchases and time between each purchase. Then you can investigate why some customers stay with you and others don’t. If the trend is negative, you can turn it around. If it’s positive, you can keep doing what you’re doing and improve on this trend.
Data science allows you to quantify the engagement levels. This metric is not focused on the purchase but can reflect customer satisfaction. It could include data such as the number of customers following you on social media, liking and commenting on your posts, resharing them, reviewing your products or services, etc. Is sharing better than liking? Is commenting better than sharing? Is a comment positive or negative? Putting value to such information that could mean everything and nothing is where data science comes in. For example, by determining the ‘feeling’ of comment, whether it is highly positive, positive, neutral, negative, or extremely negative. You can calibrate machine learning algorithms to that for you. Much faster and much more consistent. The algorithm’s worldview isn’t separated into before and after a cup of morning coffee.
One of the critical metrics is a churn rate, which gives you the ratio between newly acquired and retained customers. This also can help you detect whether there is an inflow or outflow of customers and the reasons. Without it, you could only guess. But when you find the cause of something, it’s easier to tackle its effect.
The Customer Loyalty Index is more focused on the customers’ intent (future) than on the past. In other words, how likely are they to recommend, buy from you again, and try your other products?
All these metrics help you know where you stand regarding customer loyalty. From there on, you can work on improving it. And you do that by targeting your customers with personalized offers, loyalty programs, discounts, new products, etc.
Knowing what to offer is intertwined with who you offer it to. What customers want reflects itself in every process of product development.
Knowing the customers’ needs, you can identify what is missing in the market. Is it a completely new product? Is it something already existing but with some additional features? Maybe the same features but more user-friendly? Or simply designed differently, so the customers want it?
Using data science in product development allows for much faster reactions to changes in the market and customers’ demands, which again gives your business the potential to realize sales you would otherwise miss.
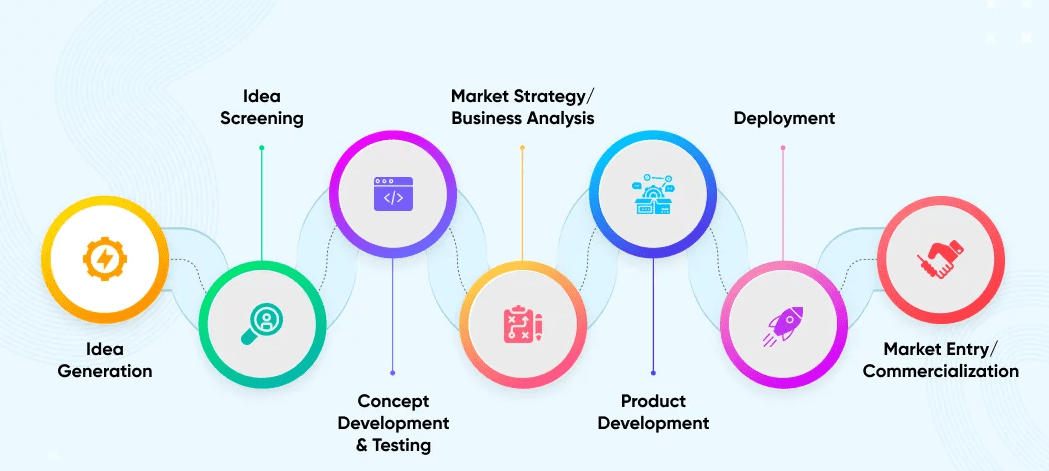
Source: https://www.netsolutions.com/insights/everything-about-new-product-development/
Looking at the product development steps, you can easily imagine that data science can help virtually every stage.
For example, analyzing the idea’s feasibility and its marketability, what your competitors are, and how to do things differently. This includes product features, design, packaging, pricing, and marketing strategy.
When screening the idea, you have to take into account what the customers want, can you offer it to them, and at what cost. Is this a great idea you have feasible and marketable? Once you analyze all data, you can start developing and testing your concept.
When you develop the concept and test it, you should again think about the benefits for the customers, are there similar products on the market, who your competitors are, and what they’re doing.
Can you offer something different to take your competitors’ market share or fit in between them? The data collected on how customers react to your concept idea can tell you what you got right. And, of course, you can enhance your concept by getting ideas from customers.
When it comes to marketing, segmentation again comes in. Who are your (potential) customers? Based on your answers, you should adapt the product design, packaging, pricing, how and where you market it, and how you distribute it to satisfy customer demand.
After you identify your market, the product can be developed based on the collected data and its analysis. This means creating functionalities according to your concept, designing the product, and testing it.
Using machine learning accelerates product design and engineering, fine-tuning and automating a product’s testing.
Relying on data science to fully or partly automate the product development process, in turn, lowers your costs, the time it takes from the idea to the product reaching the market, and the quality of your product.
This is especially true when it comes to digital products. But if you’re in manufacturing, the product development process is similar. Again, data science can be of great help. You still have to develop your product, design it, test its quality and decide on how to market it and to who.
While this is not strictly the part of data development, it has to be continuously improved for the product to acquire the market share and retain it. New features have to be added, or the existing ones improved to keep up with the competition and ever-changing customers’ tastes.
To deal with it, data science can help you with its recommendation engines that predict users’ ratings of the product (or a specific element of the product). That way, you can figure out how to improve anything related to the product and boost customer satisfaction, thus supporting your growth.
This is tightly connected to Customer Analytics but also has an additional dimension.
First, you have your customers segmented so that you can tailor your marketing approach to a specific segment. One-size-fits-all doesn’t work here!
In marketing analytics, according to Dr. Alan Zhang, you deal with:
The customer lifecycle is the aspect shared with Customer Analytics.
However, the additional element of Marketing Analytics is analyzing marketing channels. Data science is used to determine which marketing channels to use for each customer segment, when is the most suitable time to target them, which marketing campaigns to use, etc.
The metrics have to be used to evaluate the marketing decisions. Depending on the chosen channels and strategies, metrics such as click rate, bounce rate, conversion rates, unique visitors, return on investment, etc., can help you evaluate and improve your marketing decisions.
Offering the right product to the right market is also, as we saw, an internal process that can be optimized using data science. There are also other internal processes that don’t directly relate to these two business foundations but are equally important and can have an immense impact.
To satisfy the customers’ demand, you have to have inventory management in place. By using data science, you can have real-time information about your stock. From there, you can provide your customers with correct information about the availability of specific products and where to find them. You can stop stock-piling certain products that are not selling well while at the same time continuously being out of stock with a product high in demand.
You can find strategically the best locations and sizes for your warehouses and shops, the stock you keep, the number of employees to handle it, etc. This will not only allow you to quickly react to the customers’ demand changes but also predict them.
The same is with the distribution. Do you want to use your own fleet to deliver a product to your customers? Or should you use other companies’ services? The costs play a role here, but also the delivery time. Not only how fast the customer gets your product but also your delivery time estimates can be more accurate by using data. Then you can use actual delivery times to detect where your process is lacking. Analysis can lead to a decision to use your own fleet, employ more or fewer drivers, optimize their delivery routes, find new means of transportation, predict fuel costs, traffic jams, delays, etc. All that can keep your costs low while achieving the reliability and speed your customers want from you.
Connected with that, if you’re in the manufacturing industry, is using data science to predict failure rates and adapting your production lines to the demand increase or decrease.
Stating the obvious: to use data science for business growth, you’ll need data scientists. Not only them but the whole range of different experts for various positions that will be necessary as your company grows. How do you know which set of skills you need? Will the new employee perform well? Are you looking only for expertise, or does the employees’ personality factor in? Not less important, how do you keep the good ones?
Human resources management could benefit from data science. Using algorithms on data you have on the candidates will help you determine the suitable candidates in terms of their education, expertise, and personality. That way, you can predict which candidate will most probably be a top performer. This heavily changes the old way of hiring someone on gut feeling.
By using data science in training and development, you can move from one-size-fits-all. Employees are all different. They don’t learn things the same way (e.g., some like a more theoretical or practical approach), and they don’t have the same interest (e.g., some are aspiring to be leaders while some want to do their job better) or motivation (e.g., some are more motivated by money and some by learning new stuff). Tailoring training and development to each individual will result in using their potential to the maximum while, at the same time, keeping them happy. You can only benefit from a quality and satisfied worker who wants to stay at your company.
Human resources can also use data science in workforce forecasting. Hiring is an expensive process that takes time. Data science helps in predicting the need for the workforce increase. This is the function of your business growth, but other forces have to be factored in. Knowing that you’ll need more employees is one thing, but knowing the profile of your employees is another thing. What’s the situation in the employment market? Are people you need there at all? If they are, at what price? Using data science allows you to predict these variables and support your growth by hiring the right people at the right time.
A small company might not even need sophisticated reporting. Having most data in your head is easy, you approximately know where you are, and you can confidently rely on your gut feeling. As you grow, you’ll realize navigating your business without any reporting will increasingly start to feel like driving with a blindfold. During night. And in a fog. While it snows.
Having a data pipeline that leads from the data source, through its analysis, to reports, thus allowing you to make business decisions, becomes crucial. Data engineers, database designers and administrators, data analysts, statisticians, and BI developers can do wonders for you, given the right tools.
You might start from the basics and use data only for descriptive purposes. In other words, you can find out what happened.
From there on, you can use data in ever more sophisticated ways. Not only what happened, but you can gaze into the future by starting to predict what will happen, what should be done to make something happen (or not), and even finding unknown links between datasets and finding out why and how things happen.
Doesn’t this sound like any business that wants to grow would like to know?
From our point of view, data and data science had an immense impact on conducting business and, at the same time, didn’t change anything. Companies still need to have products or services and have to sell to survive and grow. However, the types of products the business can offer, how they develop them, and how they reach their customers are changing completely.
Data has had a crucial impact on how businesses are doing things. However, data doesn’t mean anything unless it’s turned into information and insights. For that, you need data scientists. Unsurprisingly, data scientists are for years high in demand. Their expertise and an ever-increasing number of data science tools can change virtually every aspect of your business: from product design, development, testing, and manufacturing, to marketing, pricing, inventory management, distribution, hiring, and reporting.
Resisting this change today is akin to shooting yourself in the foot.
Nate Rosidi is a data scientist and in product strategy. He’s also an adjunct professor teaching analytics, and is the founder of StrataScratch, a platform helping data scientists prepare for their interviews with real interview questions from top companies. Connect with him on Twitter: StrataScratch or LinkedIn.
Get the FREE collection of 50+ data science cheatsheets and the leading newsletter on AI, Data Science, and Machine Learning, straight to your inbox.
By subscribing you accept KDnuggets Privacy Policy
Get the FREE collection of 50+ data science cheatsheets and the leading newsletter on AI, Data Science, and Machine Learning, straight to your inbox.
By subscribing you accept KDnuggets Privacy Policy
Subscribe To Our Newsletter (Get 50+ FREE Cheatsheets)
Get the FREE collection of 50+ data science cheatsheets and the leading newsletter on AI, Data Science, and Machine Learning, straight to your inbox.
By subscribing you accept KDnuggets Privacy Policy
Get the FREE collection of 50+ data science cheatsheets and the leading newsletter on AI, Data Science, and Machine Learning, straight to your inbox.
By subscribing you accept KDnuggets Privacy Policy